Deep ECGNet: Ultra Short-Term Stress Monitoring
 Deep ECGNet ingests raw ECG to assess stress without HRV feature engineering.
Deep ECGNet ingests raw ECG to assess stress without HRV feature engineering.Motivation
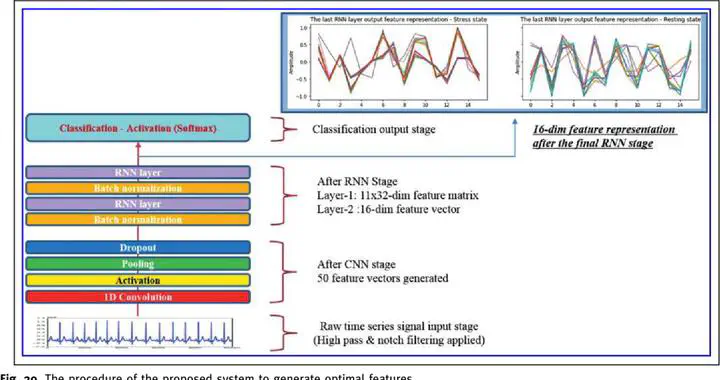
Traditional stress recognition pipelines depend on long ECG segments to extract heart rate variability (HRV) features—a process that is fragile in real-world environments. Deep ECGNet sidesteps this bottleneck by consuming raw, ultra short-term ECG signals and learning discriminative representations end-to-end.
Key Features
- Operates on compact ECG windows, enabling rapid stress estimation
- Removes the human-in-the-loop feature engineering stage
- Provides a deployable architecture for wearable devices and remote coaching platforms
Impact
Deep ECGNet proves that lightweight, high-frequency ECG segments contain enough structure for reliable stress recognition. The framework paved the way for subsequent BCML projects that monitor cognitive load, fatigue, and emotional states using fully automated neural networks.
Description
Stress recognition using electrocardiogram (ECG) signals requires the intractable long-term heart rate variability (HRV) parameter extraction process. This study proposes a novel deep learning framework to recognize the stressful states, the Deep ECGNet, using ultra short-term raw ECG signals without any feature engineering methods.